Table of Contents
Unveiling the Marvels of Bending Machines in Metal Processing
Introduction to Bending Machines
Bending machines, integral to the realm of forging machinery, stand as indispensable assets within the metal processing industry. Their versatile applications span across various sectors, including light industry, aviation, shipping, metallurgy, and beyond.
Innovations in Hydraulic Systems
The cornerstone of bending machines lies in their hydraulic systems, meticulously engineered for optimal performance. Employing piston pumps for pressure compensation and precise oil supply, coupled with throttle control for oil return, these systems epitomize energy efficiency. Furthermore, vertical hydraulic cylinders, fortified with balancing and locking mechanisms, ensure safe and reliable operation, delivering formidable clamping and shear forces for superior performance during material bending.
Design Excellence and Structural Innovation
The design intricacies of bending machines extend to press systems, sheet metal shear systems, and hydraulic pump stations. Here, meticulous attention is paid to circuit design, structural layout, and the integration of non-standard components. Through this design process, a harmonious fusion of structural compactness, rational layout, and simplified manufacturing is achieved, elevating the efficiency and operability of these machines.
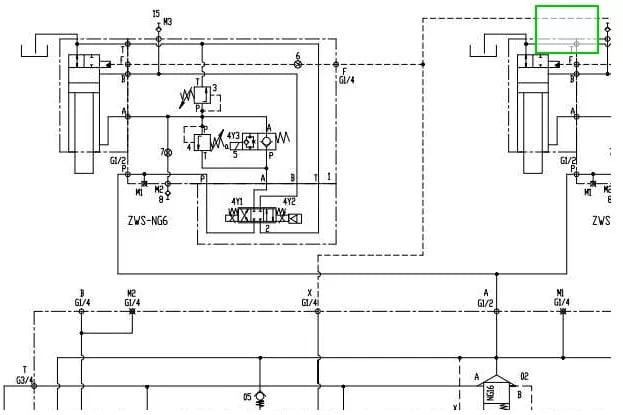
Delving into Hydraulic Systems
Exploring Fluid Power Fundamentals
Fluid power systems leverage the transmission of energy through various media, be it liquid or gas. Originating with water-based systems, the evolution of hydraulics has ushered in a new era, predominantly characterized by circuits utilizing mineral oil. Additionally, compressed air serves as another common medium, offering a viable alternative for energy transmission.
Navigating Industry Dynamics
Despite its significance, fluid power remains a realm often overlooked within the industry. With minimal dedicated personnel for circuit design and maintenance, reliance on fluid power distributor expertise is commonplace. Mechanical engineers, lacking substantial fluid power training, often turn to distributor salespersons for guidance, highlighting the need for comprehensive industry education.
Unraveling the Advantages of Hydraulic Systems
Compact, efficient, and versatile, fluid power cylinders and motors epitomize the pinnacle of modern engineering. Their ability to operate seamlessly within confined spaces, coupled with instantaneous reversibility and variable speed, renders them invaluable assets. Yet, challenges persist, primarily stemming from inadequate understanding and suboptimal circuit design, leading to issues such as overheating and leaks.
Optimizing Performance and Efficiency
Strategic Decision-Making: Hydraulics vs. Pneumatics
In navigating the choice between hydraulic and pneumatic systems, discerning the optimal force requirements emerges as a pivotal factor. While pneumatic circuits excel in low-force applications, hydraulics reign supreme in high-force scenarios. A nuanced understanding of their respective strengths and limitations informs strategic decision-making, ensuring optimal system performance.
Addressing Operational Challenges
Overcoming operational challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach, encompassing circuit design optimization and proactive leak prevention measures. By minimizing shock and ensuring cool operation, the incidence of leaks can be substantially mitigated, bolstering system reliability and longevity.
Harnessing Pascal's Law: The Bedrock of Fluid Power
At the heart of hydraulic and pneumatic systems lies Pascal's Law, a foundational principle dictating the behavior of confined fluids. This immutable law underpins the functionality of bending machines, facilitating precise control and efficient energy transmission.
Conquering Compressibility Challenges
Mitigating Compressibility: A Prerequisite for Efficiency
While hydraulic fluids are conventionally deemed incompressible, the presence of trapped air introduces a degree of compressibility. Strategic measures to minimize compressibility, coupled with meticulous circuit design, are imperative for optimizing system efficiency and performance.
Eliminating Operational Hindrances
Efforts to eliminate trapped air within hydraulic circuits represent a critical endeavor, vital for enhancing system rigidity and operational efficiency. By mitigating the adverse effects of compressibility, bending machines can operate seamlessly across diverse applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Conclusion: Pioneering the Future of Metal Processing
In conclusion, bending machines stand as veritable marvels of modern engineering, revolutionizing metal processing across myriad industries. Through relentless innovation and a steadfast commitment to excellence, these machines continue to push the boundaries of possibility, shaping the future of metalworking with unparalleled precision and efficiency. As we navigate the evolving landscape of industrial automation, the role of bending machines remains paramount, heralding a new era of ingenuity and productivity in metal processing.



