Création d'un manuel d'exploitation pour un cisaille à poutre pivotante Il s'agit de fournir des instructions détaillées sur la manière d'utiliser l'équipement de manière sûre et efficace. Voici un aperçu structuré d'un tel manuel :
Table des matières
Caractéristiques standard de la cisaille à poutres pivotantes hydraulique
Le cisaille à poutre pivotante hydraulique est conçu pour la découpe de plaques en métal-acier, avec une capacité basée sur une résistance de plaque de 450 N/mm2.
Veuillez ajuster l'épaisseur de la plaque si vous coupez d'autres matériaux avec des résistances différentes.
La machine est dotée d'une structure en tôle soudée, ce qui permet une utilisation facile et des performances fiables.
La coupe est alimentée par pression hydraulique et le retour est contrôlé par une bouteille de gaz azote, ce qui permet de protéger la machine contre les surcharges.
La machine peut être équipée d'un système d'affichage numérique ou d'un système de contrôle numérique, selon la demande du client.
Un indicateur d'écartement des lames est également fourni pour des réglages pratiques et rapides.
La machine est équipée d'un dispositif d'alignement avec éclairage et la course de coupe peut être ajustée pour améliorer l'efficacité de la coupe de plaques étroites.
De plus, des bras de support avant et une butée arrière sont fournis. La butée arrière est transférable mécaniquement et sa position peut être affichée numériquement ou contrôlée par un contrôleur NC via des encodeurs, avec micro-réglage par un volant. Les bras de support avant sont équipés de règles.
Une bille de support de matériau roulant est prévue sur la table de travail pour minimiser le glissement avec les barres en tôle et réduire la résistance au frottement.
Une clôture de sécurité a été installée pour assurer un fonctionnement sécuritaire.
Châssis de la cisaille à poutres pivotantes hydrauliques
Châssis de la machine
Plaque en acier soudé à haute rigidité comportant deux cylindres fixés sur le poteau vertical gauche et droit.
Un étau de coupe est installé sur la table de travail pour un réglage aisé de la planche de coupe inférieure, garantissant ainsi l'alignement de l'espace entre les planches de coupe supérieure et inférieure. Une boule d'alimentation est également installée sur la table de travail pour un fonctionnement pratique et rapide.
Cadre de coupe
La plaque soudée à haute rigidité est supportée par la douille excentrique (9) et entraînée par les cylindres gauche et droit et le cylindre de course pour terminer le processus de coupe par répétition pendulaire. La surface verticale du support de coupe ascendante est courbée pour maintenir l'alignement de l'espace entre la coupe ascendante et la coupe basse.
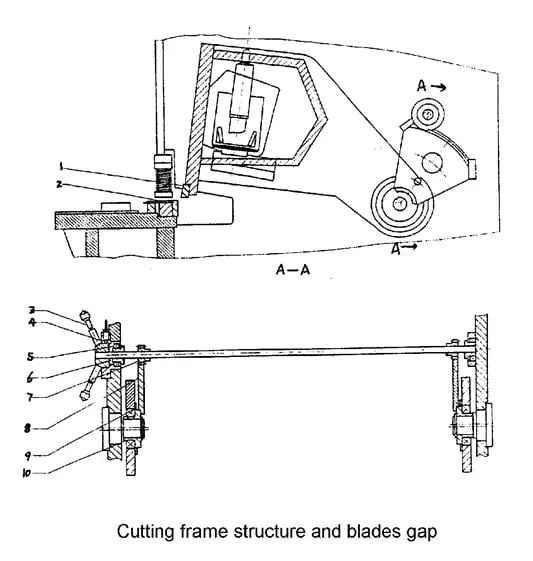
Dispositif de pression (maintenir enfoncé)
La presse est constituée de cylindres d'alimentation sous pression installés sur la plaque de support devant le châssis de la machine. Le flux d'huile dans le cylindre d'alimentation sous pression crée une pression qui pousse vers le bas contre la force de traction du ressort de contrainte (18), fixant fermement la plaque de presse. Une fois la découpe terminée, les cylindres sont réinitialisés par la force de traction du ressort de contrainte. La pression augmente avec l'épaisseur de la plaque.
Jauge avant et jauge arrière
Jauge avant :
La table de travail est équipée d'un indicateur de soupape sur la règle, ce qui permet d'ajuster la barre mobile à la soupape souhaitée. La découpe de plaques d'acier minces peut être effectuée facilement sur la jauge avant. La jauge arrière (voir photo 5) est fixée sur la planche de coupe supérieure et se déplace de haut en bas avec elle.
La butée arrière est réglée par un moteur de 0,55 kW, qui réduit le couple par l'intermédiaire d'un engrenage et entraîne la tige de commande. En appuyant sur le bouton « + » ou « - », la butée peut être réglée vers l'avant ou vers l'arrière. Si la soupape souhaitée ne peut pas être obtenue par un réglage mécanique, le volant (50) peut être tourné pour obtenir la soupape requise, ce qui rend le réglage de la butée arrière à la fois pratique et fiable.
La plage standard de la butée arrière est de 20 à 750 mm. Si la longueur de la plaque de coupe est supérieure à la distance maximale de la butée arrière, la butée arrière (43) peut être retirée jusqu'à sa position minimale et la planche peut être soulevée à l'aide de la surface inclinée du cadre de support (47), ce qui permet de couper n'importe quelle longueur de plaque. (Voir la Fig. 4)
Installation d'une cisaille à poutres pivotantes
Emballage / Expédition de la cisaille hydraulique
Toutes les machines quittant l'usine sont emballées avec un bras d'équerrage et un repose-pieds fixés au protège-main. Les outils de travail et un manuel d'utilisation sont emballés dans une seule boîte.
Toutes les surfaces exposées de la machine sont recouvertes d’un inhibiteur de rouille, qui peut être facilement éliminé avec du kérosène ou un solvant.
Levage de la cisaille hydraulique
Utilisez uniquement des câbles métalliques approuvés et sûrs pour soulever cette machine à partir des deux points de levage situés de chaque côté de la machine. (Voir Figure 5)
Fondation
Toutes nos cisailles sont conçues pour être installées sur une fondation. Veuillez vous référer au plan de fondation ci-joint pour plus de détails.
Installation
Cette cisaille hydraulique doit être correctement mise à niveau pour une performance de coupe optimale. Pour cela, utilisez une jauge de mise à niveau de haute qualité sur la zone de maintien de la plaque.
Avant de procéder à la mise à niveau, assurez-vous d'avoir cinq plaques de base (mesurant au moins 150 x 150 x 9 mm) placées sous les pieds de la machine pour éviter que les vis de nivellement ne s'enfoncent dans le sol en béton.
Une fois la machine nivelée, fixez sa position en remplissant l'espace sous et autour de ses pieds avec un mélange de coulis de ciment.
Installation électrique
Assurez-vous que l'alimentation électrique locale est compatible avec cette cisaille hydraulique avant de mettre sous tension toute alimentation électrique.
Connectez le câble d'alimentation au côté inférieur gauche du panneau électrique. Certaines machines peuvent nécessiter un fil neutre.
Réglage de la cisaille à poutre pivotante
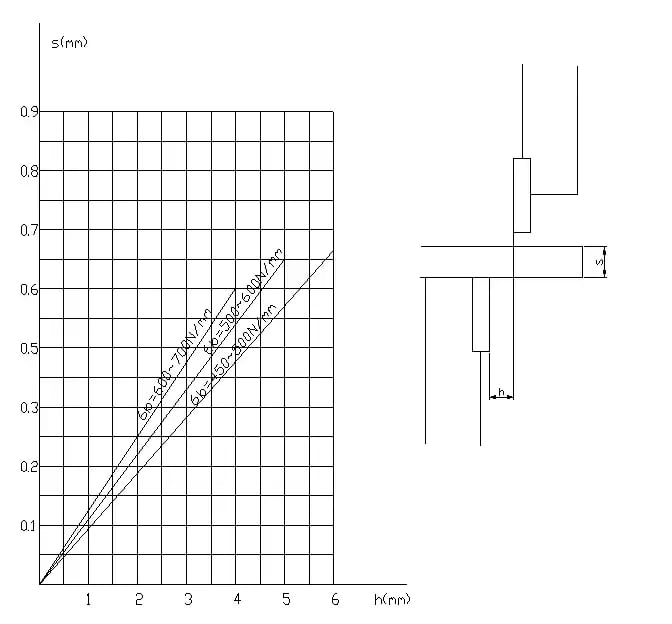
Régler l'écart entre les lames de la cisaille hydraulique
L'écartement des lames est crucial pour la qualité de la coupe et la durée de vie des lames. Veuillez effectuer le réglage en fonction du tableau de réglage de l'écartement ci-dessous.
Régler l'écart entre les lames
Pour régler l'écart (voir l'image 2), vous devez desserrer la vis serrée (4), puis tourner le volant (3) jusqu'à la valeur souhaitée, qui doit être calculée en fonction de l'épaisseur de la plaque, et enfin serrer la vis (4).
Il y a une vanne à boisseau sphérique (située sur le côté droit de la machine, à l'extérieur du cylindre) qui est utilisée pour mesurer l'espace libre entre les lames supérieure et inférieure.
Pour plus de détails : en mode manuel, lorsque le cadre de coupe atteint le point mort bas, fermez rapidement le circuit d'huile, ce qui fait que le cadre de coupe reste au point mort bas. Ensuite, ouvrez lentement la vanne à boisseau sphérique, ce qui fait que le cadre de coupe se déplace pas à pas vers le haut sur toute la course. Cela vous permettra de mesurer la valeur de jeu de l'espace entre les lames.
Fonctionnement de la cisaille hydraulique
Préparation de la machine
(1) Retirez le bras d'équerrage et la pédale de la zone de protection de la main. Fixez le bras d'équerrage sur le côté gauche de la table de la machine à l'aide de boulons et des deux trous latéraux. Le bras doit être proche du panneau électrique.
(2) Nettoyez les composants de toute huile sale, en veillant à ce que le robinet à boisseau sphérique soit en position ouverte.
(3) Lubrifiez toutes les zones nécessaires.
(4) Remplissez le réservoir d'huile avec 200 L d'huile hydraulique HL46 pour chaque machine sous le modèle 12 mm.
(5) Connectez la ligne de terre, mettez l’appareil sous tension et vérifiez le fonctionnement de tous les composants électriques.
Démarrage de la machine
(1) Appuyez sur le bouton « START » et relâchez-le.
(2) Le voyant « moteur allumé » doit s'allumer.
(3) Changez le sélecteur de mode de « MAN » à « AUTO ».
(4) Appuyez sur la pédale pour faire descendre le cadre de coupe et effectuer une coupe.
(5) Si le cadre de coupe ne descend pas, il est probable que le moteur tourne dans le mauvais sens. Coupez l'alimentation et inversez l'un des deux fils de phase pour redémarrer le moteur.
(6) Le porte-lame supérieur monte et s'arrête lorsqu'il atteint l'interrupteur de fin de course.
Butée arrière motorisée
(1) L'affichage de la butée arrière motorisée doit être réglé avec précision en usine et doit correspondre à la distance entre la barre de butée arrière et le bord de coupe.
(2) Appuyez sur le bouton « + » pour ramener la barre de butée arrière vers l'arrière. La lecture augmentera et s'arrêtera lorsqu'elle atteindra la fin de course maximale L/S 3.
(3) Appuyez sur le bouton « - » pour ramener la barre de jauge arrière vers l'avant. La lecture diminuera et s'arrêtera lorsqu'elle atteindra la fin de course minimale L/S 4.
(4) Le parallélisme de la butée arrière doit être réglé en usine, mais peut être calibré selon les besoins.
(5) Déplacez la barre de butée arrière vers l'arrière pour retirer le revêtement antirouille avant la coupe.
Note:
(1) Le tableau de pression doit être affiché pendant la découpe et la pression doit être vérifiée si elle semble incorrecte. Il peut être nécessaire de régler la soupape de trop-plein.
(2) Si un bruit inhabituel ou une surchauffe du réservoir d'huile se produit pendant le fonctionnement, la machine doit être immédiatement arrêtée. La température du réservoir d'huile ne doit pas dépasser 60°C.



