Troubleshooting a hydraulic shearing machine involves identifying and addressing common issues that may arise during operation. Here's a systematic approach to troubleshooting a shearing machine:
Table of Contents
Steps to Settle Problems of Hydraulic Shearing Machine
Commissioning
Level the shearing machine.
Fill the hydraulic oil tank, open the cover to remove any debris and clean the filter screen, then refill the oil. The type of hydraulic oil to be used depends on the model and region.
Turn on the power, check the power indicator light, activate all emergency stop switches, start the oil pump, and verify that the motor is rotating in the correct direction.
The machine tool operates at a pressure of 25 Mpa. Adjust the machine pressure according to the thickness of the plate.
Lubricate the machine according to the instructions indicated on the machine's label.
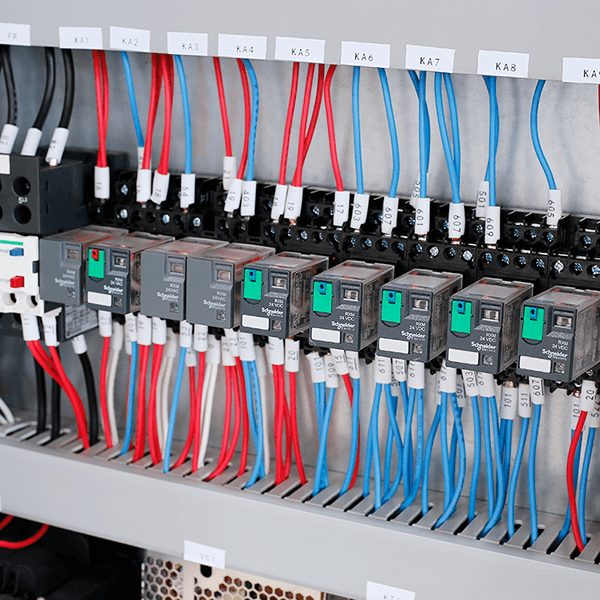
Troubleshooting
Oil Circuit:
If the machine suddenly stops working and the blade does not move up or down, first check the machine and oil circuit (solenoid valve) and foot switch.
If no faults are found in the circuit, disassemble the solenoid valve for cleaning.
Back Gauge:
If the two ends of the plate after shearing are inconsistent, check the back gauge connecting rod and see if the screws have fallen off or if the synchronous belt is slipping.
Adjust the screw of the back gauge guide to bring both ends within the acceptable error range.
If the size of the cut material is different from the value displayed on the display, inspect the encoder that connects the flexible shaft to see if it is torn or if the screws are loose.
If the connecting flexible shaft is damaged, replace it and then calibrate the value of the back gauge.
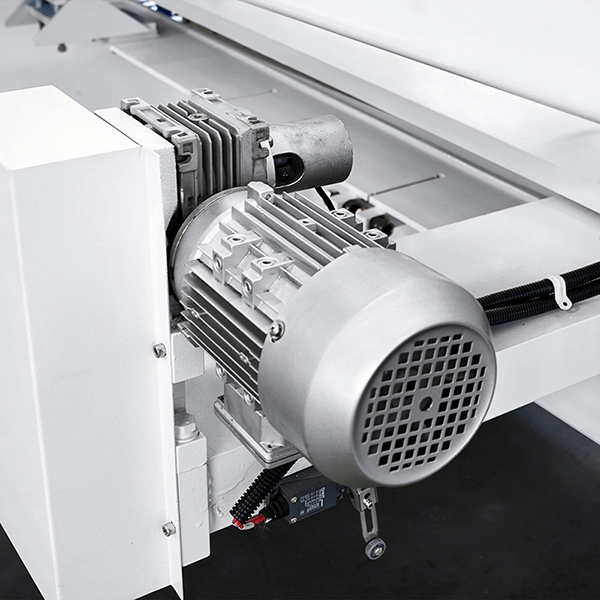
Noise
The hydraulic machine produces noise during operation. Check the oil pump of the motor for any potential noise.
Also, check the noise of the oil cylinder and return cylinder.
If the machine makes a squeaking sound, check if the ball head of the return cylinder is low on oil and if the cylinder ball head requires oil.
If the pressing cylinder lacks force, add nitrogen at 6-8 MPa.
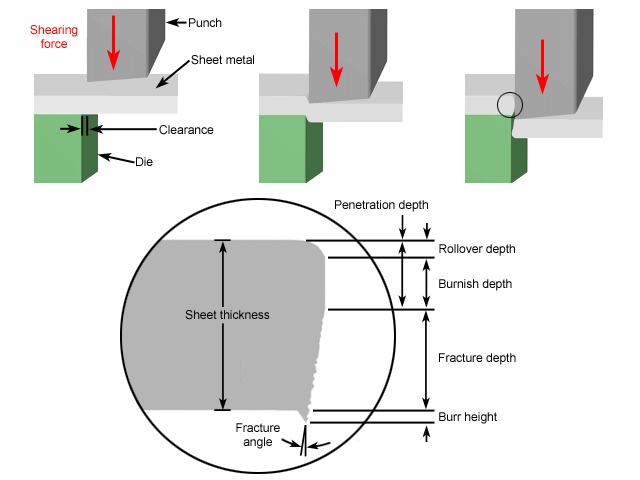
Adjustment of Blade Edge Clearance
If the blade edge is dull or the blade is not sharp, turn over the blade or replace it promptly.
When adjusting the blade edge, first set the blade edge clearance to the maximum, then gradually decrease it by closing the ball valve.
At this point, the upper and lower blades should be on the same plane. Use a feeler gauge to measure the gap between the blade edges and adjust it through the blade-adjusting screws located on the workbench.
How to Avoid Hydraulic Shearing Machine Failure
To avoid hydraulic shearing machine failure and ensure optimal performance and longevity, follow these preventive measures:
Regular Maintenance:
Implement a scheduled maintenance program as recommended by the manufacturer.
Perform routine inspections of the machine's components, including hydraulic system, blades, back gauge, and electrical connections.
Clean the machine regularly to remove debris, dust, and metal shavings that can accumulate and affect performance.
Lubricate moving parts and hydraulic components according to the manufacturer's specifications.
Monitor Hydraulic Fluid:
Check hydraulic fluid levels regularly and top up as needed to maintain proper levels.
Monitor the condition of the hydraulic fluid and replace it at recommended intervals to prevent contamination and degradation.
Inspect Blades and Cutting Components:
Regularly inspect the condition of the blades for signs of wear, damage, or dullness.
Sharpen or replace blades as needed to maintain cutting accuracy and prevent uneven cuts.
Ensure proper alignment of blades and adjust blade clearance as necessary for different material thicknesses.
Calibrate Back Gauge and Hold-Down System:
Regularly calibrate the back gauge to ensure accurate positioning of the material for cutting.
Verify that the hold-down system is securely holding the material in place during cutting to prevent slippage and misalignment.
Check Electrical Components:
Inspect electrical connections, switches, and controls for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
Tighten loose connections and replace worn-out components to prevent electrical failures.
Operate Within Specified Parameters:
Follow the manufacturer's guidelines and operating instructions when using the hydraulic shearing machine.
Avoid exceeding the machine's rated capacity or cutting parameters, as this can lead to premature wear and potential failure.
Monitor cutting speed, feed rate, and material thickness to ensure they are within acceptable limits.
Train Operators:
Provide comprehensive training to operators on the proper operation and maintenance of the hydraulic shearing machine.
Emphasize safety procedures and best practices to prevent accidents and damage to the machine.
Address Issues Promptly:
Promptly address any abnormal sounds, vibrations, or performance issues observed during machine operation.
Investigate the root cause of the problem and take corrective action to prevent further damage or failure.
By following these preventive measures and maintaining regular upkeep of your hydraulic shearing machine, you can minimize the risk of failure and ensure consistent performance in your metalworking operations.
Conclusion
Debugging and troubleshooting of the hydraulic shearing machine encompasses checks of the oil cylinder, oil circuit, and back gauge, as well as addressing issues such as noise and blade clearance adjustments.
The quality of the shearing machine also plays a role in the cost of repairs and maintenance.
By choosing KRRASS's hydraulic shearing machine, you can benefit from time and cost savings, as well as receive high-quality after-sales service.
For more information about our shearing machines, please visit our contact us page.



