An electric press brake is a type of machine used in metalworking and sheet metal fabrication for bending and shaping sheet metal. Unlike traditional hydraulic press brakes that use hydraulic fluid to generate force, electric press brakes utilize an electric motor to drive the bending process. These machines are known for their precision, speed, and energy efficiency.
Table of Contents
Key features of an electric press brake include enhanced accuracy in bending angles and dimensions, faster cycle times, and improved energy efficiency compared to hydraulic counterparts. Electric press brakes may also offer automation features, allowing for programmable control and increased productivity.
The transition to electric press brakes represents a notable evolution in metal fabrication technology, providing manufacturers with advanced capabilities for various bending applications. As technology continues to advance, electric press brakes are expected to undergo further refinements and innovations, contributing to improved efficiency and performance in the field of metalworking.
Development History
The concept of press brakes dates back to the early 20th century, but the first iteration of electric press brakes only surfaced in the late 1990s.
As technology advanced, the traditional hydraulic press brakes started being replaced by electric alternatives, offering more precision and energy efficiency.
The 21st century brought significant advancements in the realm of electric press brakes. The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices led to the increasing adoption of electric machines, with companies seeking lower energy consumption and reduced maintenance costs. This drive for innovation and eco-friendliness set the stage for the swift evolution of electric press brakes.
Components
An electric press brake is comprised of several critical elements:
Frame
The frame of the electric press brake is its skeleton, typically composed of a robust material like steel. It provides the necessary stability and rigidity, enabling the machine to withstand the force exerted during operations.
Ram
Also known as the top beam, the ram is a crucial component responsible for delivering the downward force required to bend the sheet metal.
Bed
Situated opposite the ram, the bed or the bottom beam provides a base for the sheet metal to rest on during the bending process.
Backgauge
The backgauge is an adjustable fence, guiding the positioning of the sheet metal. It ensures consistent and precise bends.
Control System
In electric press brakes, the control system plays a vital role in coordinating all operations, enabling the control of ram movement, backgauge positioning, bending angles, and more.
The control system of an electric press brake generally includes a numerical control unit (CNC), servo motors, a back gauge system, and a foot pedal. The CNC unit acts as the brain of the operation, directing other components to execute specific tasks.
Now, let’s break down these components:
- CNC Unit: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) is a sophisticated system that uses computer programming inputs to dictate the movement and operation of machinery. The CNC unit of an electric press brake allows for precise control of bending angles, depth, and speed, hence enhancing productivity and precision. Almost all modern electric press brakes are some type of CNC press brake.
- Servo Motors: Servo motors translate the commands from the CNC unit into physical motion. In an electric press brake, servo motors are responsible for driving the ram (upper tool) up and down with remarkable speed and accuracy.
- Back Gauge System: This system is vital in positioning the workpiece accurately before bending. Controlled by the CNC, it moves the workpiece to the correct position based on programmed dimensions.
- Foot Pedal: This allows the operator to have hands-free control over the ram’s movement, ensuring safety and enhancing convenience during the operation.
Electric Motor
Electric press brakes leverage an electric motor for power, providing a clean, efficient and reliable energy source. It replaces the hydraulic pumps used in traditional hydraulic press brakes.
Tooling
Tooling is a crucial aspect that includes all replaceable bits involved in the bending process. It encompasses the punch (which aligns with the ram) and the die (which aligns with the bed).
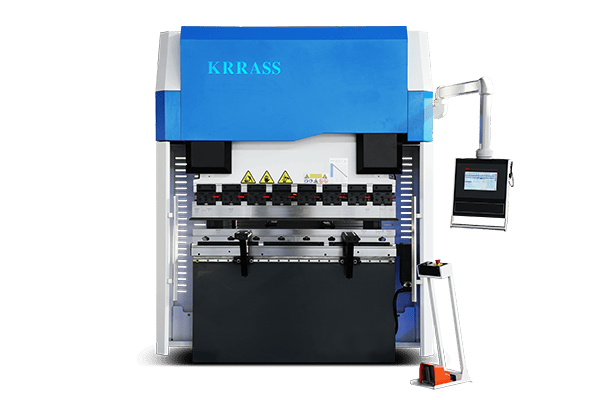

Working Principle
An electric press brake, in its essence, utilizes a set of mechanical components to exert force upon a sheet of metal for creating precise bends.
However, the heart of its operation lies in its electric motor, which drastically sets it apart from its hydraulic counterpart.
- An electric press brake works on the principle of mechanical force being transferred through a set of ball screws, which are powered by an electric motor.
- The motor provides rotary motion, which is converted into linear motion by the ball screws, driving the ram downwards to create a bend on the metal sheet placed on the bed.
- Unlike a hydraulic press brake, where oil is used to transfer the energy, electric press brakes employ mechanical components and electricity, reducing the scope of oil leaks and ensuring cleaner operations.
- The digital control system allows for precision in bending, as it can accurately control the ram’s position and speed.
Types Optional
Electric press brakes come in various forms, including Servo-Electric, Electro-Hydraulic, Hybrid, and Direct Drive Electric Press Brakes, each with unique characteristics and advantages.
Servo-Electric Press Brake
A servo-electric press brake is a subcategory within the electric press brake family, powered by servo motors. These machines provide high-speed bending operations. These motors move the ram through the use of a ball screw or a belt drive mechanism, translating the motor’s rotary motion into the linear motion needed for bending.
Their defining characteristic is their energy efficiency: the servo motors only consume electricity when the ram is in motion, significantly reducing overall energy consumption. Furthermore, the absence of hydraulics in their operation makes them a cleaner and more environmentally friendly option.
Electro-Hydraulic Press Brake
Bridging the gap between traditional hydraulic press brakes and fully electric models, electro-hydraulic press brakes bring together the best of both worlds. They use hydraulic systems driven by electric servo motors, combining the power and force capacity of hydraulics with the precision and energy efficiency of servo-electric systems.
These machines offer higher levels of accuracy and repeatability than traditional hydraulic press brakes, all while maintaining similar tonnage capabilities. The servo-electric motor powering the hydraulics allows for precise control and reduces the idle energy consumption considerably.
Hybrid Press Brake
The hybrid press brake is another fusion of hydraulic and electric technologies. In a hybrid system, a small quantity of oil is used, pressurized by a bank of electrically driven hydraulic pumps.
This system offers many of the advantages of an all-electric press brake, such as decreased energy consumption and high precision, while retaining the raw power and force of hydraulic systems. It is an ideal choice for manufacturers seeking a balanced solution with the strengths of both hydraulic and electric press brakes.
Direct Drive Electric Press Brake
Direct drive electric press brakes employ a motor directly connected to the ram, eliminating the need for a pulley system. This results in less energy loss, making these machines incredibly energy efficient.
Direct drive mechanisms allow for a more precise control over the bending process, making it a suitable option for manufacturers seeking high accuracy and energy efficiency. With fewer moving parts than other types, they are also easier to maintain and offer a longer lifespan.
Pros & Cons
Electric press brakes offer numerous benefits, some of which include:
- Energy Efficiency: Electric press brakes consume less energy compared to their hydraulic counterparts, leading to cost savings and a reduced environmental footprint.
- Precision: The advanced control systems in electric press brakes provide superior precision and repeatability, crucial in high-quality metal fabrication.
- Speed: Electric press brakes are known for their high speed, bolstering productivity levels.
- Lower Maintenance: Unlike hydraulic press brakes, electric press brakes do not require regular oil changes, leading to reduced maintenance costs.
- Noise Reduction: Electric press brakes operate with less noise, contributing to a more pleasant working environment.
Despite their many advantages, electric press brakes also come with certain downsides:
- High Initial Investment: Electric press brakes typically require a higher initial investment compared to hydraulic models.
- Complexity: The advanced control systems of electric press brakes can be complex, requiring specialized training for operators.
- Repair Costs: Given their sophisticated components, repair costs can be higher if an electric press brake malfunctions.
- Limited Tonnage: For extremely high-tonnage applications, hydraulic press brakes may still be the preferred option due to their superior force.
The lifespan of an electric press brake can vary greatly, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years. This is contingent on factors such as usage intensity, maintenance, and the quality of components used.
Range of Cost
Electric press brake prices can vary widely based on type, capabilities, and manufacturer. On average, you can expect to pay:
- Servo-Electric Press Brake: $50,000 – $200,000
- Electro-Hydraulic Press Brake: $70,000 – $250,000
- Hybrid Press Brake: $90,000 – $300,000
- Direct Drive Electric Press Brake: $100,000 – $350,000
How to Choose an Electric Press Brake?
When selecting an electric press brake, consider factors like the required bending force, bending length, accuracy needs, energy efficiency, available space, and budget.
Also, consider the reliability and reputation of the manufacturer.
A notable example is KRRASS, one of the world’s top 10 manufacturers in the steel metalworking machinery realm. Founded in 1995, KRRASS was among the earliest batch of sheet metal working machine manufacturers producing CNC press brakes and fiber laser cutters in China. We strive to make bending and cutting sheet metal a quick, precise, and reliable process, thereby making their clients more productive and competitive.
The versatility of KRRASS electric press brakes for sale is evident in their broad range of models with capacities varying from 30 to 2000 tons.
Apart from KRRASS, there are a variety of reliable electric press brake manufacturers in the global market. The decision will primarily depend on the specific requirements of your manufacturing process, budget, and after-sales service.
Electric vs. Hydraulic Press Brake
- Energy Efficiency: Electric press brakes consume significantly less energy compared to hydraulic press brakes. The servo motors in electric press brakes only consume power during the bending process, resulting in up to 50% energy savings.
- Precision and Control: Electric press brakes offer greater precision. Their advanced control systems and servo motors ensure high repeatability, precision, and control over the bending process.
- Maintenance: Electric press brakes have fewer moving parts and don’t require hydraulic oil. This results in reduced maintenance costs and downtime.
- Speed: Electric press brakes often provide higher speeds and quicker acceleration and deceleration times, leading to improved productivity.
- Noise Pollution: Hydraulic brakes tend to be noisier during operation than electric press brakes, which could be a critical factor depending on the work environment.
However, it’s worth mentioning that the initial investment for electric press brakes may be higher than hydraulic ones, and for extremely high tonnage requirements, hydraulic press brakes might still be the preferable option.

Conclusion
The evolution of metal fabrication technology is evident in the remarkable advancements brought about by the electric press brake. Offering heightened precision, increased speed, and enhanced energy efficiency, these machines stand out as superior alternatives to traditional hydraulic press brakes. Nonetheless, it is crucial to recognize that they come with their own set of drawbacks, necessitating careful consideration before making an investment.
A comprehensive understanding of the fundamental components, operational principles, as well as the advantages and disadvantages associated with electric press brakes empowers manufacturers to make well-informed decisions. Various factors, including environmental considerations and the choice of a reputable manufacturer, play pivotal roles in unlocking the full potential of these cutting-edge machines.
As technology continues its relentless progression, one can anticipate further refinements and innovations within the realm of electric press brakes. This ongoing evolution holds the promise of continually enhancing productivity and profitability in the field of metal fabrication.



