Table of Contents
Overview
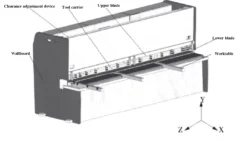
A hydraulic shearing machine is a type of machine that uses a moving upper blade and a fixed lower blade to apply a shearing force to metal plates of varying thicknesses, resulting in the separation of the plates into the desired size by utilizing an appropriate blade clearance.
Shearing machines are a type of forging machinery that mainly perform metal processing. They are widely utilized in various industries such as aviation, light industry, metallurgy, chemical industry, construction, shipbuilding, automobile, electric power, electrical appliances, decoration, and more, to provide specialized machinery and complete equipment sets.
What is Hydraulic Shearing Machine?
The hold-down cylinder of a hydraulic shearing machine is powered by the hydraulic system to clamp down on the steel plate, and the left and right cylinders drive the movement of the blade up and down.
hydraulic shearing machine
The hold-down cylinder of the hydraulic shearing machine operates under the power of the hydraulic system to clamp the metal sheet in place, while the left and right oil cylinders control the movement of the blade, moving it up and down.
The upper blade on the blade carrier and the lower blade fixed on the blade holders have a suitable clearance to apply shear force to metal sheets of various thicknesses and cut them to the desired size.
The hydraulic shearing machine is used for direct shearing of a variety of metal materials to meet the demands of industries such as steel production, shipbuilding, automobile manufacturing, container production, electrical switch appliances, machinery manufacturing, and light industry.

Working Principle of Shears
The working principle of a hydraulic shearing machine involves the use of hydraulic power to apply force to shear or cut sheet metal or other materials. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a hydraulic shearing machine operates:
Material Placement:The sheet metal or material to be cut is placed on the cutting bed of the hydraulic shearing machine.
Clamping:The material is securely clamped in place using a hold-down system to prevent movement during the cutting process.
Hydraulic System Activation:The hydraulic system of the machine is activated, typically by a motor-driven hydraulic pump. This pressurizes the hydraulic fluid (usually oil) and generates hydraulic pressure within the system.
Blade Positioning:The upper blade (also known as the moving blade) and lower blade (stationary blade) are positioned based on the desired cutting length and angle. The upper blade is connected to a hydraulic cylinder or ram, which controls its movement.
Shearing Process:When the hydraulic system is activated, the hydraulic cylinder applies downward force to the upper blade, causing it to descend towards the lower blade.
Material Separation:Once the shearing process is complete, the upper blade returns to its original position, and the material is released from the clamping system.
Control and Monitoring:The operation of the hydraulic shearing machine is controlled and monitored using a control panel or interface. Operators can adjust parameters such as cutting length, angle, and blade clearance to achieve the desired cutting results.
Safety Measures:Hydraulic shearing machines are equipped with safety features such as safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and light curtains to ensure operator safety during operation.
As the upper blade moves downwards, it exerts pressure on the material positioned between the blades, initiating the shearing process.
The material is sheared or cut as it passes between the upper and lower blades. The blades have sharp edges that penetrate and separate the material along the desired cutting line.
The sheared material is removed from the cutting bed, and the process can be repeated for additional cuts or operations.
Overall, the hydraulic shearing machine utilizes hydraulic power to generate force and shear sheet metal or other materials with precision and efficiency. This makes it a versatile and essential tool in various industries, including metal fabrication, manufacturing, and construction.
Types of Shears
Hydraulic shearing machines come in various types, each designed for specific cutting applications and requirements. Here are some common types of hydraulic shearing machines:
Fixed Rake Hydraulic Shear: In a fixed rake hydraulic shear, the rake angle (the angle of the upper blade) remains constant during the cutting process. This type of shear is suitable for general-purpose cutting of sheet metal and offers simplicity and ease of operation.
Variable Rake Hydraulic Shear: Variable rake hydraulic shears allow for the adjustment of the rake angle of the upper blade. This feature enables operators to optimize the cutting performance for different materials, thicknesses, and cutting conditions. Variable rake shears offer greater flexibility and versatility compared to fixed rake shears.
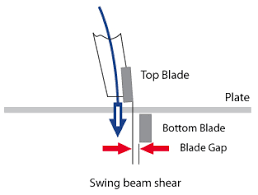
Swing Beam Hydraulic Shear: Swing beam hydraulic shears feature a swinging or pivoting upper beam that moves in an arc-like motion during the cutting process. This design allows for increased clearance between the blades, making it easier to cut thicker materials and reduce distortion. Swing beam shears are suitable for cutting medium to heavy-duty materials.
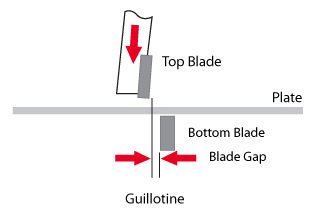
Guillotine Hydraulic Shear: Guillotine hydraulic shears have a straight, vertical blade motion for cutting sheet metal. The upper blade moves in a straight downward motion to shear the material against a stationary lower blade. Guillotine shears are commonly used for high-speed, precision cutting of thin to medium thickness materials.
CNC Hydraulic Shear: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) hydraulic shears are equipped with automated controls and programmable features for precise and repeatable cutting operations. They allow for the programming of cutting parameters, such as cutting length, angle, and blade clearance, to achieve accurate and efficient cutting results.
Angle Hydraulic Shear: Angle hydraulic shears are specialized shearing machines designed for cutting angle iron or other structural steel profiles. They feature blades specifically shaped to accommodate the profile of the material being cut, allowing for precise and clean cuts.
Hydraulic Plate Shear: Hydraulic plate shears are heavy-duty shearing machines designed for cutting thick plates or large metal sheets. They typically have a robust frame and powerful hydraulic system capable of exerting high cutting forces to shear through heavy materials with ease.
Hydraulic Guillotine Shear: Hydraulic guillotine shears combine the features of a guillotine shear with the power and precision of hydraulic operation. They are suitable for cutting a wide range of materials and thicknesses and offer high-speed and accurate cutting capabilities.
Each type of hydraulic shearing machine has its advantages and is suitable for specific cutting applications. The choice of machine depends on factors such as the type and thickness of materials to be cut, production volume, precision requirements, and budget constraints.
Advantages of Hydraulic Shearing Machine
Compared to traditional plate shears, hydraulic plate shears have a significant advantage in that they are controlled by a series of codes during operation. These codes are generated through various combinations of characters and depend on the specific work requirements.
One major benefit of using code to control the hydraulic shearing machine is the ability to accurately control the orientation, speed, and strength of the machine. This is achieved through numerical control, which uses computer programming to operate the machine through numerical combinations.
In terms of positioning, the hydraulic shearing machine has clear advantages. The adjusting rod can rotate continuously around the central axis without dead angles, and the machine operates quietly, providing a peaceful work environment that doesn’t affect the mood or health of the operators.
The machine is made from durable stainless steel with strong corrosion resistance and stability, even in environments with high vibration amplitudes. The operation of the machine is simple and easy to learn, requiring computer skills to operate it.
Additionally, the machine not only has strong functionality but also boasts a sleek appearance.
In terms of safety, great progress has been made with the hydraulic shearing machine being equipped with a sturdy self-defense fence. In the event of machine failure, the fence separates the operator from the machine.
The adjustment of light also greatly improves speed, allowing for quick movement to the correct position for a clearer view of the work situation, adding convenience to the production process and operation of the machine.
Applications of hydraulic shearing machine
Hydraulic shearing machines find wide-ranging applications across various industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and precision in cutting sheet metal and other materials. Some common applications of hydraulic shearing machines include:
Metal Fabrication:Hydraulic shearing machines are extensively used in metal fabrication workshops for cutting sheet metal into precise shapes and sizes. They are employed for cutting materials such as mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, among others, to produce components for machinery, appliances, automotive parts, and structural assemblies.
Construction:In the construction industry, hydraulic shearing machines are utilized for cutting metal sheets and plates to fabricate structural components, building facades, roofing materials, and reinforcement bars. They are also used for processing metal components used in infrastructure projects, such as bridges, tunnels, and roadways.
Manufacturing:Hydraulic shearing machines play a crucial role in manufacturing operations across various sectors, including aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and furniture. They are used for cutting metal sheets and panels to manufacture components, enclosures, housings, and casings for products ranging from electronic devices to furniture pieces.
Shipbuilding:In shipbuilding and maritime industries, hydraulic shearing machines are employed for cutting metal plates and profiles used in the construction of ship hulls, decks, bulkheads, and superstructures. They enable the precise shaping and fitting of metal components required for vessel construction and repair.
Automotive:Hydraulic shearing machines are integral to automotive manufacturing processes for cutting sheet metal components used in vehicle bodies, chassis, frames, panels, and interior parts. They are utilized in stamping and fabrication operations to produce parts with tight tolerances and complex shapes required for modern automobiles.
Appliances and Electronics:Hydraulic shearing machines are utilized in the production of household appliances, electrical enclosures, and electronic devices. They are used for cutting metal sheets and panels to manufacture components such as appliance housings, cabinets, control panels, and mounting brackets.
Metal Recycling:Hydraulic shearing machines are employed in metal recycling facilities for cutting and processing scrap metal into manageable sizes for recycling. They are used to shear metal scrap such as old vehicles, appliances, and industrial equipment into smaller pieces that can be melted down and reused in the production of new metal products.
Custom Metal Fabrication:Hydraulic shearing machines are utilized by custom metal fabrication shops and jobbing workshops to produce a wide range of custom-made metal components and structures according to specific design requirements. They enable the efficient and precise cutting of metal materials for bespoke projects and prototypes.
Conclusion
Hydraulic shearing machines are commonly used in industries such as metal fabrication, manufacturing, construction, automotive, and aerospace for cutting sheet metal, plates, and other materials to produce components, parts, and assemblies.