A press brake machine is a piece of industrial equipment used in metalworking and sheet metal fabrication to bend and shape sheet metal. It applies force to deform the material, creating bends, angles, or other shapes according to the desired specifications. Press brakes are a key component in the manufacturing of various metal components and structures. They are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and general manufacturing.
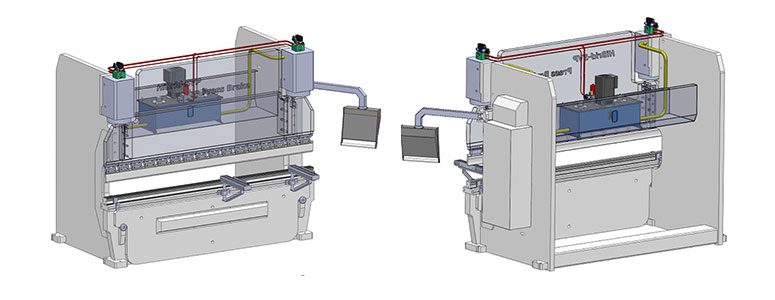
Here are the main components and features of a press brake machine:
Frame:
The frame provides the structural support for the press brake. It is designed to handle the bending forces and maintain the machine's stability during operation.
Hydraulic System:
Press brakes typically use hydraulic systems to generate the force needed for bending. The hydraulic system consists of cylinders, pumps, valves, and hoses that work together to apply controlled pressure to the metal.
Ram or Slide:
The ram, also known as the slide, is the moving part of the press brake that comes down to apply force to the sheet metal. It is controlled by the hydraulic system and can be adjusted to achieve different bending angles.
Bed and Beam:
The bed and beam are the two horizontal components that support the sheet metal during bending. The bed is stationary, while the beam moves (controlled by the ram) to perform the bending operation.
Clamping System:
The clamping system secures the sheet metal in place during bending. It prevents the material from shifting or moving during the application of force.
Backgauge:
Many press brakes are equipped with a backgauge, which is an adjustable stop that helps position the sheet metal accurately for repetitive bends. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) press brakes often have programmable backgauges for increased precision.
Control Panel:
The control panel allows the operator to set and adjust various parameters, such as bending angle, ram speed, and backgauge position. CNC press brakes have more advanced control systems for automated and precise bending.
Tooling:
Press brake tooling includes punches and dies that shape the sheet metal during bending. Tooling choices depend on factors such as material type, thickness, bend radius, and application requirements.
Safety Features:
Press brakes are equipped with safety features such as guards, emergency stop buttons, and light curtains to ensure the safety of the operator during machine operation.
Press brakes come in various sizes and configurations, ranging from small manual machines to large CNC-controlled systems capable of handling heavy-duty metal sheets. The choice of press brake depends on the specific requirements of the application and the volume of production.
How to choose Press Brake machine dies?
Choosing the right press brake machine dies, also known as punches and dies, is crucial for achieving accurate and high-quality bends in sheet metal. Here are some key considerations to help you choose the appropriate dies for your press brake machine:
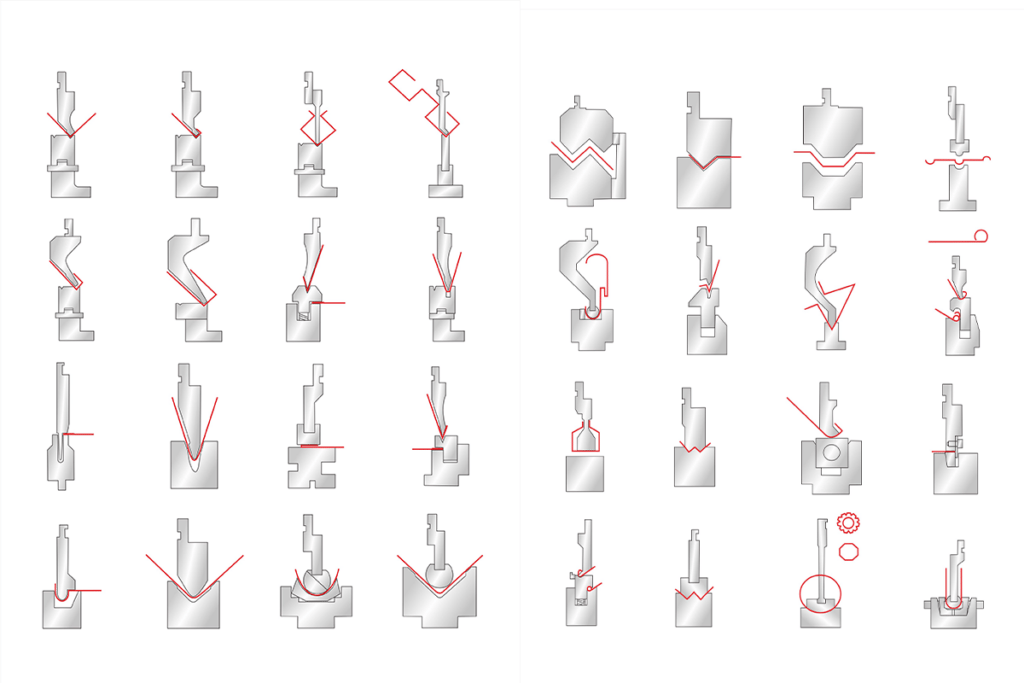
Material Type:
Consider the type of material you'll be working with (e.g., mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum). Different materials have varying properties, and choosing dies compatible with the material ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Bend Radius and Angle:
The bend radius and angle required for your application will influence the choice of dies. Select dies that match the desired bend radius and angle. Different die configurations (sharp, radius, or beveled) are available for various bending needs.
Sheet Thickness:
Choose dies with the appropriate capacity for the thickness of the sheet metal you'll be bending. Using the correct die capacity ensures consistent and accurate bends without causing damage to the material or the tooling.
Tooling Style:
Press brake dies come in various styles, such as V-dies, hemming tools, radius tools, and more. The choice depends on the specific bending needs of your application. For example, V-dies are commonly used for standard bends, while hemming tools are suitable for creating hems on sheet metal edges.
Die Length:
Consider the length of the die based on the size of the press brake and the length of the bends you need to make. Longer dies may be required for bending longer sheets or achieving specific bend configurations.
Tooling Coating or Surface Treatment:
Some dies feature coatings or surface treatments designed to reduce friction, prevent galling, and extend tool life. Coatings like nitriding or specialized coatings with low friction properties can improve performance and durability.
Material Hardness:
Tooling materials with higher hardness are generally more wear-resistant and suitable for processing harder materials. Consider the hardness of the die material based on the hardness of the sheet metal being bent.
Multi-V Die Sets:
Multi-V die sets offer versatility by allowing you to achieve various bend angles and radii without changing the tooling frequently. They are useful for applications with diverse bending requirements.
Precision and Tolerance Requirements:
If your application demands high precision and tight tolerances, select dies that meet these requirements. Precision-ground tooling helps achieve consistent and accurate bends.
Tooling Compatibility:
Ensure that the chosen press brake dies are compatible with your specific press brake model and design. Check for tooling standards like European (Promecam/Amada) or American (Trumpf) style.
Specialized Tooling:
For unique or specialized applications, consider using custom or specialized dies designed to meet specific bending challenges.
Consult the press brake manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations for die selection, and consider seeking advice from experienced operators or tooling specialists. Regular inspection and maintenance of the press brake dies are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.



